Rate of reaction is how quickly a reaction takes place. There are a variety of factors that effect the rate of reaction; but firstly, it's important to know what a Boltzmann distribution is;
 |
| (This makes a good thumbnail) |
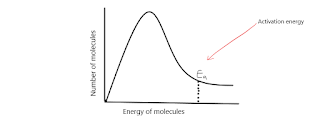
A Boltzmann distribution is a graphical way of showing molecules and their relative energies in a certain state. The scientist Robert Zartman carried out an experiment to show that all particles have different energies. He heated tin in an oven and then fired these particles at a rotating disk with a slit in it. The fastest particles went straight through the slit, the slower ones following behind but travelling through the slit at a different point on the rotation therefore landed in a different place on the disk behind (see diagram below).
 |
| Click on the images to see them larger |
Boltzmann distribution plot the number of molecules (on the y axis) against the energy of particles (on the x axis).
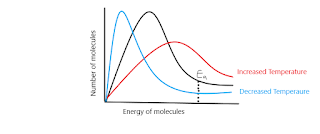
- Temperature; increasing the temperature of a reaction will cause the particles in the reaction to have higher kinetic energy. This will cause them to vibrate and move around more, increasing the chances of collision. This will then cause the rate of reaction to increase as more frequent collisions cause more successful collision, ultimately leading to an increase in the rate of reaction. It's notable that even though temperature may increase , this could affect the yield of products, especially if the reaction is exothermic. We can view particle energy and the relation to temperature on a Boltzmann distribution;
- Catalysts; catalysts lower the activation energy in a reaction by providing an alternative pathway for chemical reactions. This allows more molecules to be able to overcome the activation energy and be able to react. Introducing a catalyst increases the rate of reaction (for both sides of a reaction). There are also a variety of reasons why many industrial reactions use catalysts;
- Catalysts are reusable therefore aren't wasted in the process, although thy need to be replaced frequently as they can become contaminated by external factors.
- Catalysts allow reactions to take place at lower temperatures as high temperatures are often needed to overcome the activation energy in endothermic reactions. This reduces the pollution from generating the heat and also reduces the cost of heating the reaction.
- Catalysts are biological enzymes, meaning they are needed to convert a substrate into the correct produce for a reaction.
- Catalysts allow specific, different reactions to take place; different products may be formed under different conditions meaning different catalysts create different desired products.
- Shining light; shining light can often help initiate a chemical reaction and allow reactions to take place. The most common example of this is the initiation, propagation and termination of chlorine and hydrogen (forming radicals), see below;
- Concentration; increasing concentration of a certain molecule will increase the rate of reaction because more molecules are available to react and therefore are more likely to collide successfully and form products.
- Pressure; increasing pressure will ultimately increase the rate of reaction because molecules are closer together therefore have a higher chance of colliding compared to a lower pressure. This means that more successful collisions are likely to occur forming the products. However, like temperature, pressure can affect the equilibrium position and therefore the yield of products.
- Surface area; the higher the surface area of the molecules, the more molecules are exposed to react therefore the rate of reaction will increase.






Comments
Post a Comment